Choosing a heating system can feel a bit tricky, especially when you’re just starting to look at options. Many people find comparing Oil Filled Radiators vs Gas Central Heating (Explained) confusing because there’s a lot of information, and it can seem technical. But don’t worry, this guide will break it all down simply, helping you see the pros and cons of each choice. We’ll cover everything you need to know, step-by-step. Let’s start by looking at what makes each system tick.
What Are Oil Filled Radiators?
Oil filled radiators are portable electric heaters that heat a room using thermal oil to store and distribute heat. They’re a common choice for smaller spaces or supplemental heating because they’re easy to use. The oil inside gets heated by an electric element, then circulates to warm the radiator’s metal fins. The metal then radiates heat, warming the surrounding air. This process continues even after the radiator is turned off, providing a steady, gentle warmth. These radiators are known for their quiet operation and are a safe option for homes.
Oil filled radiators are known for being energy-efficient and safe, making them a popular option. They don’t use a lot of power, so they help save on energy costs, especially when used for short periods. They are also known for being portable, so they can be easily moved from one room to another. This makes them versatile. However, their heating output is often lower than central heating systems, which may not be ideal for larger spaces or colder climates. Let’s explore their details in the next section.
How Oil Filled Radiators Work
The heating element inside an oil filled radiator heats a special type of oil. This oil has high thermal properties, meaning it can store a lot of heat. This heated oil circulates within the radiator, warming the metal fins. The fins then radiate heat into the room. This process allows the radiator to continue radiating heat even after it’s unplugged. The oil inside the radiator is sealed, so it doesn’t need to be refilled. These radiators are designed to be safe, with automatic shut-off features to prevent overheating.
- Heating Element: This is the component that uses electricity to heat the oil. It’s typically a metal coil.
- Thermal Oil: A special oil with a high heat capacity.
- Metal Fins: These fins increase the surface area for heat radiation.
- Thermostat: Controls the temperature of the radiator.
The heating element is the heart of an oil filled radiator. It converts electrical energy into heat energy, warming the oil inside the unit. These elements are usually made of nickel-chromium alloy because of their ability to withstand high temperatures and resist corrosion. The size and power of the heating element determine the radiator’s heating capacity. They are designed to be energy-efficient and safe. The element is usually encased within the radiator’s design to prevent direct contact, enhancing safety. Over time, these elements can degrade, affecting the radiator’s performance.
The thermal oil inside the radiator plays a key role, absorbing and retaining heat. This oil is usually a non-toxic mineral oil. It is chosen for its ability to withstand high temperatures without breaking down and its good heat transfer properties. The oil circulates within the radiator, carrying heat to the metal fins. Because of its high specific heat capacity, the oil allows the radiator to continue emitting heat even after it is unplugged. The oil’s properties also contribute to the radiator’s quiet operation, since there are no moving parts. The type of oil used is usually sealed inside the unit. It does not need to be replaced.
The metal fins are essential for efficient heat transfer. They are usually made of steel or aluminum, which are good conductors of heat. The fins increase the surface area available to radiate heat into the room. They are designed to allow air to flow between them, helping to distribute the heat evenly. The design of these fins also influences the radiator’s overall size and weight. More fins mean a larger heating surface, but it can also make the radiator heavier. The fins also help with convection, where heated air rises and circulates around the room.
A thermostat is a vital component that lets you control the temperature. This device monitors the room temperature and regulates the radiator’s heating element to maintain a consistent temperature. As the room heats up to the set temperature, the thermostat automatically turns off the heating element. When the room cools down, the thermostat turns it back on. Some radiators have simple adjustable thermostats, while others come with digital controls. These digital thermostats often have timers and multiple heat settings, offering more precise control and energy efficiency. The thermostat’s accuracy plays a role in the heater’s energy consumption.
Pros and Cons of Oil Filled Radiators
When picking a heating solution, weighing the pros and cons is important. Oil filled radiators offer advantages like easy portability and safe operation, making them a good option for certain situations. However, consider their limitations, like slower heating and potentially higher running costs for larger areas. Evaluating these factors will guide you toward the best choice for your needs. Choosing the right heating solution depends on your individual needs and the space you need to heat.
- Pros:
- Portability: Easy to move from room to room.
- Safe Operation: They generally have safety features like automatic shut-off.
- Quiet Operation: They operate silently.
The portability of an oil filled radiator is one of its major strengths. Their compact design and wheels make it simple to transfer them from one room to another, or even between different floors. This is especially helpful if you only need heat in certain areas of the house. This flexibility makes them ideal for temporary heating solutions, like supplementing the main heating system or heating a guest room. Because they don’t require installation, they can be plugged in and used immediately. This convenience is a great benefit for renters or those who need a flexible heating option.
Safety is a significant advantage of oil filled radiators. They are designed with safety features that make them a secure option for homes. Most models include automatic shut-off mechanisms that activate if the unit overheats. The sealed oil doesn’t pose any fire hazards, and the surface temperatures are usually moderate, reducing the risk of burns. They are designed for quiet operation and do not produce dangerous fumes or emissions. These features make them a safe option for families with children or pets.
The quiet operation of an oil filled radiator is a pleasant benefit, especially for environments where silence is important. Unlike fan-forced heaters that can generate noise, these radiators heat the room without any sound. The absence of noise makes them great for bedrooms, offices, or living areas where you want to maintain a calm atmosphere. The design of these radiators means that the heating process is silent, using convection and radiation to heat the space, instead of noisy fans.
- Cons:
- Slower Heating: They take longer to heat a room compared to gas.
- Limited Heating Capacity: Not ideal for large areas.
- Running Costs: Electricity can be expensive, leading to higher bills.
One of the drawbacks of oil filled radiators is their slower heating pace. Unlike gas heaters or forced-air systems that rapidly heat a room, oil filled radiators take more time to reach the desired temperature. This is because the oil needs to be heated first, and then the metal fins gradually radiate heat. This slower heating can be a drawback if you need heat quickly. It makes them more suitable for maintaining a consistent temperature. However, if you require immediate warmth, other heating solutions might be more appropriate.
Oil filled radiators are often less effective for larger spaces. Their heating output is often lower than central heating systems or gas heaters. They’re usually designed for smaller to medium-sized rooms, such as bedrooms, offices, or living rooms. When used in a large space, the radiator might struggle to raise the temperature to a comfortable level. This limitation makes them best suited for spot-heating or as a supplemental heating source rather than a primary heating system for a whole house. For larger areas, you might need multiple units or more powerful heating options.
The running costs of oil filled radiators can be a consideration. Since they run on electricity, the price of heating depends on the cost of electricity in your location. The cost of using electric heaters can be higher than using gas heaters. The cost effectiveness of using oil filled radiators also depends on how frequently and for how long you use them. For regular or extended use, the electricity costs can add up. It is important to compare the energy consumption of different models and to consider using the heater in conjunction with other heating systems to reduce costs.
What Is Gas Central Heating?
Gas central heating is a system where a gas-powered boiler heats water, and this heated water flows through pipes to radiators located throughout a home. The radiators then release heat, warming the rooms. This type of heating provides even warmth across the entire house and is usually more powerful than portable heating options. Gas central heating is a popular choice for homes because of its efficiency and ability to maintain a comfortable temperature.
Gas central heating systems offer efficient and even heating across a home, and they are usually a cost-effective option for large spaces. They usually deliver higher heat output and can be controlled centrally through a thermostat, providing consistent temperatures. However, installation requires professional expertise, and the systems need regular maintenance. Let’s look at the details in the following sections.
How Gas Central Heating Works
Gas central heating involves a central boiler that heats water, and this heated water is then distributed throughout the home via a network of pipes to radiators. The heat from the water warms the radiators, which then radiate heat into the rooms. A thermostat controls the system, and it ensures that a constant temperature is maintained throughout the entire house. The system offers efficient and consistent heating.
- Boiler: This unit heats water using natural gas.
- Pipes: They carry hot water to radiators.
- Radiators: These units release heat into the rooms.
- Thermostat: It controls the temperature of the system.
The boiler is the heart of the gas central heating system. It uses natural gas to heat water, which is then distributed throughout the house to the radiators. Modern boilers are designed for high efficiency, reducing energy waste and lowering fuel costs. They burn natural gas to heat a heat exchanger. This heat exchanger then transfers heat to the water in the system. The efficiency of a boiler is rated as a percentage, with higher percentages indicating greater efficiency. Boilers come in various types, including combi boilers, system boilers, and regular boilers, each suitable for different home setups.
Pipes are important for gas central heating, as they transport the hot water from the boiler to the radiators, and then back again. These pipes are usually made of copper or plastic, which are designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures. Proper insulation of the pipes is crucial to reduce heat loss during transit. The system layout is often designed to allow efficient water flow. The pipes are usually routed through walls, floors, or ceilings, connecting the boiler to all the radiators in the house. The way the pipes are laid out affects both the heating effectiveness and the efficiency of the system.
The radiators are placed strategically throughout the house to distribute heat. They receive hot water from the boiler through the pipes. The radiators are designed to transfer heat efficiently into the rooms through radiation and convection. They can be made of steel or aluminum, and come in various sizes and styles to fit different interior designs. As the hot water circulates through the radiator, the metal heats up and radiates heat into the surrounding air. The radiators are usually equipped with valves that let you control the heat output from each unit, giving you more control over the comfort of each room. Regular maintenance, such as bleeding the radiators, is needed to ensure efficient operation.
The thermostat is your control center for gas central heating. It monitors the room temperature and signals the boiler to turn on or off to maintain a constant temperature. Most modern thermostats are digital and include features such as programmable settings, allowing you to set different temperatures for different times of the day. This can help improve energy efficiency by reducing energy usage when you are not home. Smart thermostats can also be connected to the internet, providing remote control and advanced energy-saving features. Precise thermostat control guarantees optimal comfort, while also playing a role in the system’s energy efficiency.
Pros and Cons of Gas Central Heating
Selecting between gas central heating and other options requires a look at both the benefits and drawbacks of each. Gas central heating provides advantages such as consistent and efficient heating, which makes it a popular choice. However, the installation cost, the need for professional installation, and regular maintenance are factors you should keep in mind. Careful consideration of these points will help you determine the best option to heat your home.
- Pros:
- Efficient Heating: Quickly heats the entire home.
- Consistent Temperature: Maintains a uniform temperature throughout the house.
- Cost-Effective: Usually cheaper to run than electric heating.
Gas central heating is known for its ability to heat the whole house quickly and efficiently. The boiler generates a large amount of heat, which is then distributed to radiators throughout the home. This quick and even heating means that all rooms reach the set temperature. This is especially useful in colder climates or during winter, when a fast heating response is needed. The efficiency of gas central heating systems, especially with modern condensing boilers, makes them a cost-effective option for heating large homes.
One of the biggest benefits of gas central heating is its ability to maintain a constant temperature throughout the house. With radiators in every room, the system distributes heat evenly, eliminating cold spots. The thermostat helps regulate the temperature. This uniform heating creates a comfortable living environment, allowing you to have a consistent warmth without large temperature variations. This consistent environment is particularly valuable in terms of comfort, health, and energy efficiency.
Gas central heating is usually a more economical option compared to electric heating, especially in areas where natural gas is accessible. The cost of natural gas is often lower than the price of electricity. Modern condensing boilers can achieve high levels of energy efficiency, reducing fuel consumption and lowering utility bills. When evaluating the total cost of heating, it’s necessary to consider the initial installation costs. But the ongoing savings on fuel costs can make gas central heating a sensible choice for long-term heating needs. Regular maintenance and servicing are needed to ensure the system is running at its best.
- Cons:
- Installation Costs: Professional installation is needed, which is expensive.
- Professional Maintenance: Requires regular servicing and maintenance.
- Limited Portability: It’s a permanent, stationary system.
The initial expense of installing gas central heating is a significant factor. The process needs professional expertise, which can involve significant labor and material costs. This includes installing the boiler, laying pipes, and installing the radiators. The overall costs can also depend on the size of the house, the number of radiators required, and any adjustments needed to existing systems. The installation cost can be a barrier for homeowners. However, it’s important to see this cost in terms of a long-term investment, since the fuel efficiency of gas central heating often results in savings on energy bills.
Gas central heating needs routine service to ensure proper and safe operation. This involves professional inspections and servicing of the boiler. Gas boilers need yearly checkups to keep them in good working order, which includes cleaning and checks for safety. Regular maintenance helps prevent potential issues, like carbon monoxide leaks. It also ensures the system is running at its best efficiency. This routine maintenance adds to the overall cost of owning a gas central heating system. However, it is essential for the system’s effectiveness and longevity and the safety of the household.
Gas central heating systems are not movable. They are permanently installed, which makes them less flexible compared to portable heating options. Once installed, the system is fixed in place, and you can’t easily move it from room to room, or take it with you if you move house. This lack of portability is a disadvantage if your heating needs are temporary or if you live in a rented property. Because it is a fixed system, you are limited by the initial design. You can’t easily change the heating arrangement as your needs change. This fixed aspect of gas central heating means that it’s designed to suit a specific space and permanent usage.
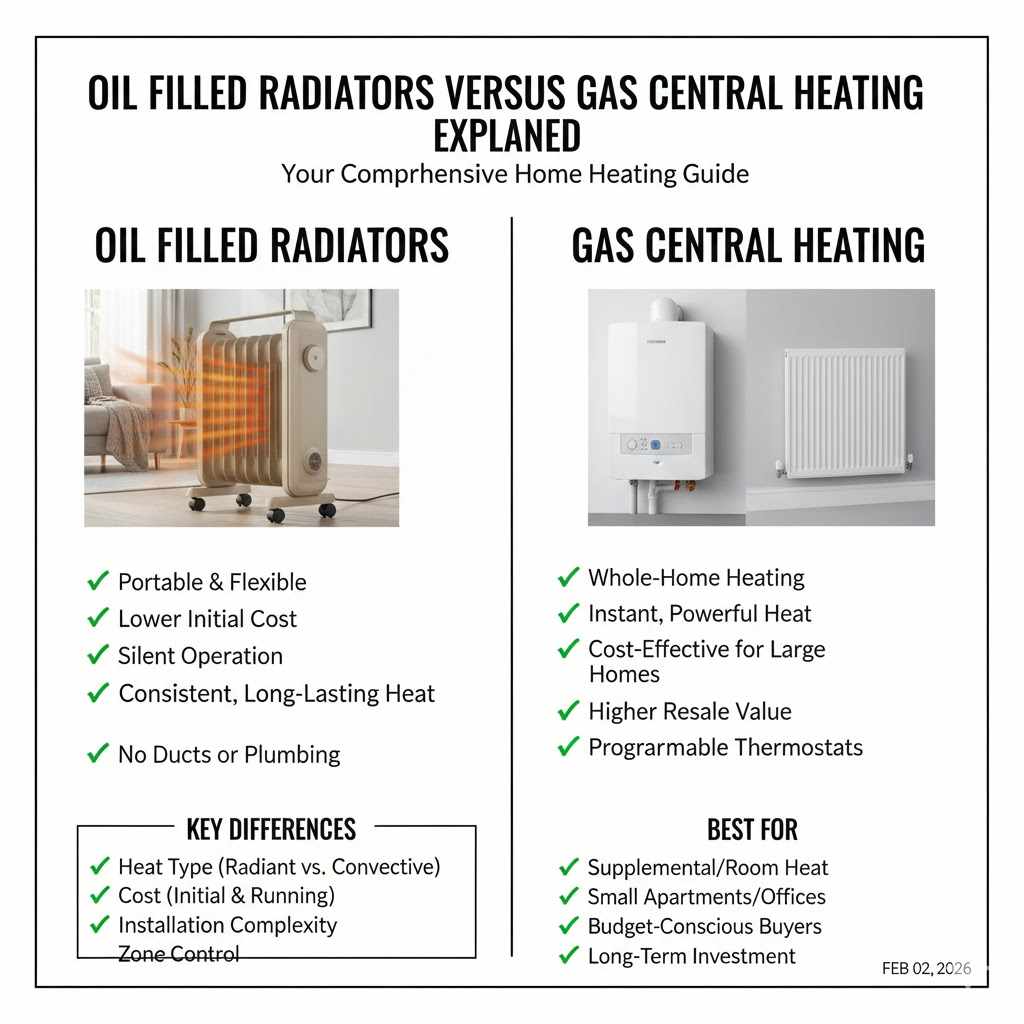
Oil Filled Radiators versus Gas Central Heating: Which Is Better?
Choosing between Oil Filled Radiators vs Gas Central Heating (Explained) depends on your specific needs and situation. Oil filled radiators are great for small spaces and provide portable heating, while gas central heating is ideal for whole-house, efficient heating. When deciding, consider factors like the size of your space, budget, and how often you need to heat your home. Understanding these key differences will help you make the best choice.
| Feature | Oil Filled Radiator | Gas Central Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Electric, uses thermal oil | Gas-powered boiler heats water |
| Heat Distribution | Radiates heat from metal fins | Hot water circulated through radiators |
| Installation | Plug-and-play, no installation needed | Professional installation required |
| Portability | Highly Portable | Fixed, non-portable |
| Heating Capacity | Suitable for small to medium rooms | Effective for whole houses |
| Heating Speed | Slower to heat | Faster to heat |
| Energy Efficiency | Varies depending on use, often good for spot heating | Efficient, especially with modern boilers |
| Running Costs | Can be more expensive, depending on electricity rates | Usually more cost-effective |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Requires regular servicing |
Consider the following to help you decide:
- Size of Space: How big is the area you need to heat?
- Heating Needs: Do you need a permanent or temporary solution?
- Cost: Factor in both upfront and ongoing costs.
The size of your living space is a key consideration. Oil filled radiators are best for heating small spaces, like bedrooms or home offices. They might not be effective for heating larger areas, like open-plan living rooms or entire houses. Gas central heating is designed to heat the whole home efficiently, making it the better choice for larger properties. Consider the square footage of the area you want to heat. If you need to heat multiple rooms consistently, gas central heating is likely the better choice. If you only need to heat a single room, an oil filled radiator might be adequate.
Think about how you plan to use the heating system. Oil filled radiators are a great solution for occasional or supplemental heating. They are easy to move. They can be used to heat a room as needed. Gas central heating, on the other hand, is a permanent solution for whole-house heating. It is perfect if you need consistent warmth throughout your home, especially during the colder months. Consider how frequently you need heat. If you only need it now and again, oil filled radiators might be suitable. For continuous heating, gas central heating is usually the best option.
The financial side is a major factor when choosing a heating system. Oil filled radiators have low upfront costs. They only need to be plugged in. However, the running costs can be higher, depending on the price of electricity. Gas central heating has higher initial installation costs. But it can be more cost-effective to run, especially with modern, efficient boilers. Consider your budget. Look at energy rates in your area. Look at how long you plan to live in your home. Factor in ongoing maintenance costs. The total cost of heating includes both upfront investments and the ongoing costs of fuel, maintenance, and electricity. This will help you make an informed choice.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: Are oil filled radiators safe to use?
Answer: Yes, oil filled radiators are generally very safe. They don’t get as hot as other types of heaters. They have safety features like automatic shut-off to prevent overheating, and the oil is sealed within the unit.
Question: Is gas central heating energy-efficient?
Answer: Yes, modern gas central heating systems are designed to be energy efficient, especially when using condensing boilers. These boilers can recover heat that would otherwise be lost, improving overall efficiency.
Question: How long does an oil filled radiator take to heat a room?
Answer: Oil filled radiators take a bit longer to heat a room compared to other types of heaters. They usually take about 15-30 minutes to warm up. The time also depends on the size of the radiator and the size of the room.
Question: How often should a gas central heating system be serviced?
Answer: It’s recommended to have your gas central heating system serviced by a qualified professional at least once a year. This checkup ensures that the system is operating safely and efficiently and it can also prevent bigger problems.
Question: Can I use oil filled radiators as the primary heating source for my home?
Answer: While you can use oil filled radiators, they are best suited for smaller rooms or supplemental heating. They are often not powerful enough to heat an entire house, especially during colder months. For primary heating, gas central heating is usually a better option.
Final Thoughts
When selecting between Oil Filled Radiators vs Gas Central Heating (Explained), consider your individual needs and the spaces you need to heat. Oil filled radiators offer portability and safety, making them a good choice for smaller areas. Gas central heating provides whole-house warmth and can be more cost-effective, but involves a larger initial investment and professional servicing. Assess your heating needs, space size, budget, and long-term goals to make the best decision for your home. By evaluating the pros and cons of each choice, you can ensure a warm and comfortable environment that suits your lifestyle. Don’t be afraid to compare different models and get professional advice to confirm your decision.